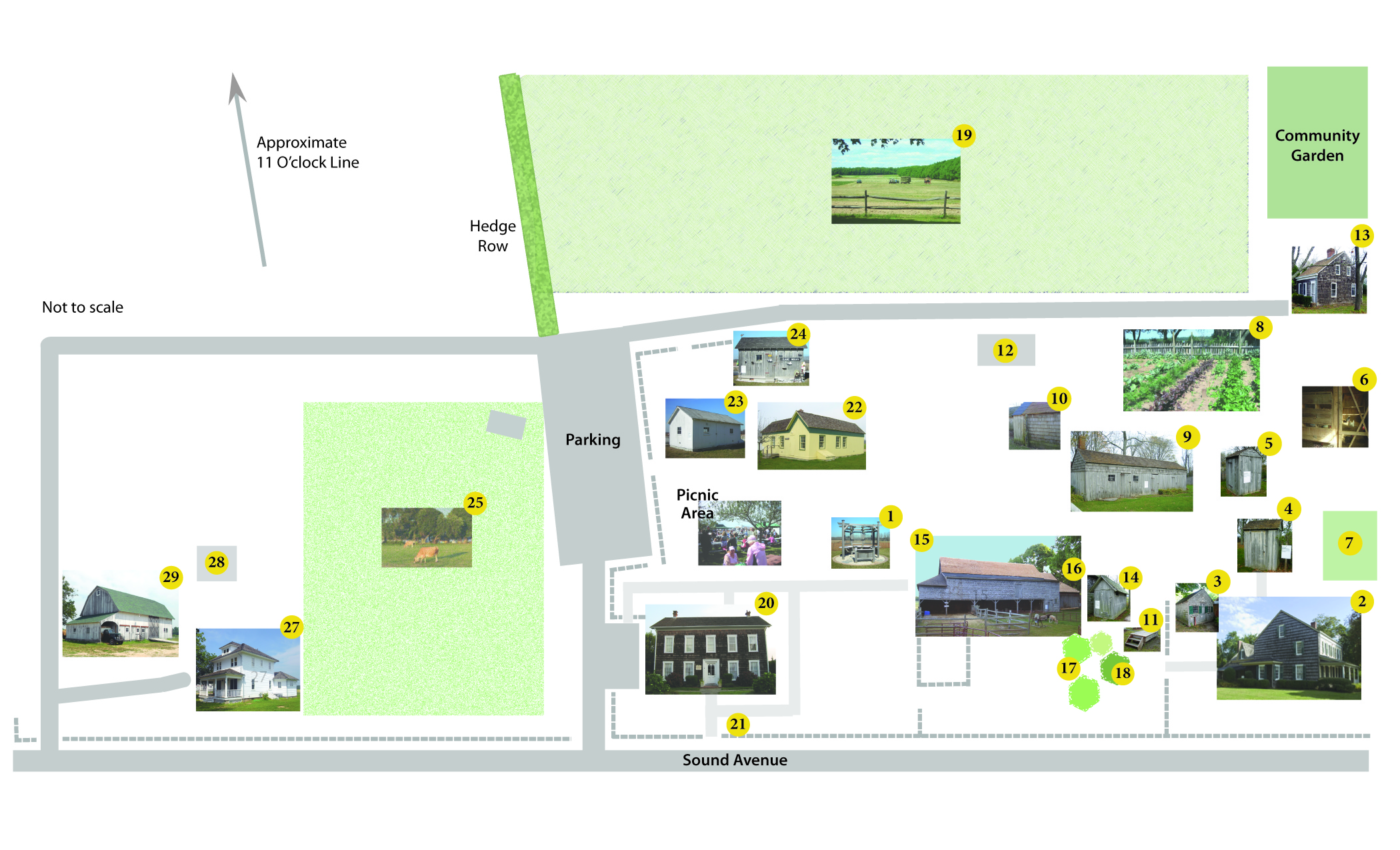
Welcome to Hallockville Museum Farm! We have 19 buildings on 28 acres of preserved farmland telling the story of over 250 years of farming on Long Island’s North Fork. Use this brochure to walk through that history, starting with the mid-18th century Hallock farmstead on the eastern end of the campus and ending with the mid-20th century Cichanowicz farmstead on the west side. Along the way, learn how the families that farmed these fields built and continuously modified their homes, barns and outbuildings as the local community, economy and fashion changed over the centuries.
Building interiors are only accessible during docent-led tours.
1. Interpretive Kiosk. From the visitor center in the Hudson-SydIowski House, follow the sidewalk east. Your first stop is the Hallockville Museum Farm’s interpretative kiosk. It tells the story of the museum and surrounding landscape over the last 300 years. Stand in the middle and look out through the east window toward Hallock Home-stead to see the last load of corn going to market in 1926 or look the other way towards the Cichanowicz farmhouse to see truckloads of potatoes and cauliflower parked in font of their garage in 1941. The kiosk was designed by Fred Blumlein Associates and constructed by museum volunteers and members of the original “Regina Maris Crew,” now known as the “Tuesday Crew” with funding from the Trust for Public Land and Verity O’Brien.
2. Hallock Homestead. From the Kiosk, walk around the front of the barn and continue through the fence to the side door of the Hallock Homestead. Reuben Brown constructed the first part of this house about the time of his marriage to Elinore Youngs in 1765. The Hallock family acquired the property in the 1790s and grad-ually expanded and “modernized” it over the next century. The family built a small wing on the west side for “Grandpa” Zachariah about 1833 that later was moved across the road. In 1845, Herman Hallock took possession, and son David Halsey Hallock’s family resided there until 1979 when the last Hallock, daughter Ella at age 95, vacated. They “raised the roof” of the original story-and-a-half “Cape Cod” style house to create the two-and-a-half story house visible today. In 1860, the family moved the small west wing to the rear to make way for a larger addition on the west for David Halsey Hallock and his first wife, Marietta Terry. In 1903, the wing was moved across the street and converted into a single-family house that burned in 1938. Over the years, the family made many other changes, culminating with a front “piazza” (porch) in 1907. It provided a pleasant place to sit and chat to friends as they passed nearby in their carriages.
Shoemaker’s Shop. Attached to the side porch of the Homestead is Capt. Zachariah Hallock’s shoemaker’s shop where he made approximately 1,700 shoes and boots between 1771 and 1820. It originally stood on the south side of Sound Avenue. About 1860, the Hallocks moved the building to this site, and converted it to a “milk house” with a cellar under it to keep dairy products cool.
4. Outhouse. Behind the Homestead is the original four-seater family outhouse. Note the two doors—in case one was blocked by snow! The Hallocks told stories of having to tunnel from the house to the outhouse in the famous blizzard of 1888.
5. Smokehouse. Just east of the outhouse is a reconstruction of the original smokehouse used for curing pork and fish. Smokehouses often caught fire and were generally located a safe distance from the main house and barn. The fire pit can be seen on the east side of the building.
6. Chicken Coop. Just beyond the smokehouse is a reconstruction of the original chicken coop. Poultry houses always faced south to take full advantage of the winter sun. Fencing kept the chickens from predators, but not necessarily keeping a chicken or two from escaping.
7. Homestead Gardens. In front of the chicken coop is a garden maintained by the Hallockville volunteers. This is the site of the original family gardens – conveniently near the kitchen door. Plants are typical of those found in a 19th century garden.
8. Heirloom Garden. The Hallockville Gardeners have established and maintain a vegetable garden featuring “heirloom” varieties. The heirloom crops are typically open pollinating, nonhybrid plants grown from seeds that have not been genetically altered and have been passed down through generations. Garden implements are manual and labor is intensive, but productive.
9. Workshop/Woodshed. Walk back around the rear of the Homestead to the long narrow building. The east end was the washhouse in the mid-19th century, with a wood stove for boiling clothes. The cistern partially visible below provided rain-water, preferred to “hard” well water, for washing clothes. The family added a more “modern” washroom to the Homestead kitchen in 1894 and converted this to a farm shop. Late in the 19th century, the Hallocks added the right half of the structure to store wood for their stoves
10. Homestead Garage. Immediately west of the workshop is the garage the Hallock family built about 1920 to house their first automobile, a Model T Ford. Look at the back end to see how it was later enlarged as the family’s cars grew longer.
11. Horseblock. Follow the old driveway towards Sound Avenue to a reconstruction of the original horse block, which made it easier for women with long dresses to climb into wagons or mount horses. The picket fence is a reconstruction of the original picket fence built around the homestead in the late 19th century. Also note the stone walkway. Herman Hallock brought these stones back from Connecticut for this purpose.
12. Hog House. The “Tuesday Crew” built this hog house on the concrete foundations of the original hog house. Hogs were important on farms not only as a source of meat for family or market, but also as a way to recycle food waste from the kitchen and fields.
13. Bethuel E. Hallock House. Just beyond the fence is the house built on the south side of Sound Avenue about 1837 for the grandson of Captain Zachariah Hallock. Later in the 19th century it became the home of the Irish-American Gilson family. It now serves as staff housing for the museum. PLEASE NOTE THIS IS A PRIVATE RESIDENCE.
14. Corncrib. At the corner of the barn is a wooden corncrib that was originally located on the Dayton farm in Mattituck (later owned by the Lomaga family who donated it to Hallockville). Farmers cut corn stalks in late summer and stacked them in shocks or teepees. When the corn was dry, they harvested the ears, husked them and stored them in the corncrib. The slatted sides of the crib kept rain out while allowing air to flow through.
15. Homestead Barn. Like most early barns in the area, the original Homestead Barn built in 1765, stood near the road. The family moved it back to the current location about 1860, in part to facilitate the construction of a cellar under it to store potatoes that were then becoming important crop on the farm. The Hallocks gradually expanded the original three-bay 1,000-square-foot English style bam in all directions until it covered 5,000 square feet by the early 20th century. This open south-facing shed was designed to shelter cows and sheep during cold winter months.
16. East Shed. This is the newest part of the bam. The Hallock family owned shares in the “Iron Pier” constructed nearby on Long Island Sound in 1901 by a company of local farmers. When ice destroyed the pier in 1904, the Hallocks used salvaged lumber to build this shed to house their farm wagons and equipment.
17. Tree Grove. David Halsey Hallock (1838-1939) planted many of the trees in this grove, including a rare Shag Bark Hickory whose seed he brought back from Connecticut. American Walnut, three American Basswoods (commonly known as Linden), two Horse Chestnuts and several Norway Maples. Unfortunately, the Butternut tree he brought back from his honeymoon trip to Ohio in 1866 has disappeared.
18. American Elm. The tree just outside the gate is an American Elm, a tree once common in the area, but now a rare survivor of the Dutch elm disease.
19. Hallock Farm Fields and Icehouse. Walk past the sheep pen and around to the rear of the bam. In the second half of the 19th century, the Hallocks cut blocks of ice from Hallock Pond on the north end of their farm (near Long Island Sound). It was stored in an icehouse near this site (no longer in existence). Straw insulation preserved the ice through the summer. The Hallock farm stretched to Long Island Sound, about a mile to the north, and extended about the same distance south of Sound Avenue, and was approximately 150 acres in all in the late 19th century. Principal crops were potatoes, hay, corn, wheat, cattle and cordwood.
If you wish, wander out into the fields where museum volunteers grow hay on several acres of the fields for the farm animals. Several more acres are leased to a local farmer to grow vegetables, and a small potato patch is maintained by our neighbors–the Long Island Antique Power Association. Also, take a look at our Community Gardens in the southeast corner where individuals can rent a patch to grow their own produce with excess given to a food pantry.
20. Hudson-Sydlowski House. About 1840 Samuel Hudson constructed a simple story-an-a-half house about a half-mile to the west of the museum. The Hudson family “raised the roof” in the late 1870s to make it a stylish two-story house. The German-immigrant Berg family lived in the house from 1885 to 1927, followed by the Polish-immigrant Sydlowski family who acquired and lived in it for most of the rest the 20th century. It was moved to Hallockville in 1991. To the east of the house, is a small garden maintained by the Hallockville Gardeners. Currently, it serves as the administrative offices, meeting room and gift shop.
21. Milestone. In front of the Hudson-Sydlowski house is an original Sound Avenue milestone erected in 1838 by the Town of Riverhead when Zachariah Hallock II was a highway commissioner. It stood opposite the museum’s east boundary and shows the miles east to Greenport and west to Wading River.
22. Aunt Frances’s Washhouse/Trubisz Little House. The oldest part of this structure may date to early 19th century or perhaps the late 18th. It was substantially enlarged and remodeled about 1860 for use as “Aunt” Frances Hallock’s washhouse on the farm just to the east of the museum. In the 20th century, it served as the “little house” on the farm of the Polish-immigrant Trubisz family. It was moved to the museum and restored in 2003 by the “Tuesday Crew.” Currently, it houses the Trubisz family exhibit and the annual Hallockville local history exhibits.
23. Trubisz Sprout House. This building was built on the Trubisz farm just to me east of the museum to replace a structure destroyed by the 1938 hurricane. The family packed Brussels sprouts here in the winter. The basement housed their water pump. It is currently used as a venue for children’s camps and activities
24. Combs Decoy Shop. This structure was originally the farm shop on the Overton family’s circa 1876 “gentleman’s estate” in Peconic. This was the carving shop of Captain Jack Combs, a descendant of a long line of Great South Bay decoy carvers. Jack Combs moved the building to the museum in 2004, restored it to carve traditional decoys here.
25. Cichanowicz Pasture. Hallockville’s two Jersey cows graze in the pasture just west of the main parking lot with two bovine friends. Information about Jersey cows can be found on the back of the cowshed, built in 2006 by the “Tuesday Crew” and Hallockville volunteers.
26. West Hedgerow. This hedgerow starts at the northwest corner of the parking area, follows an “eleven o’clock line” marking the west side of the Hallock farm for centuries. As is typical of old hedgerows, it includes a wide variety of native plants such as sassafras, smooth sumac, locust, black cherry, mockernut hickory and poison ivy. The Cichanowicz family bought the 35-acre farm on the west side of the hedgerow about 1923. It stretched to Long Island Sound and included half of Hallock Pond.
27. Cichanowicz House. Walk along the farm road on the back side of the pasture to the white Cichanowicz farmhouse. When Konstanty and Adela Cichanowicz, both Polish immigrants, bought this farm about 1923, the original circa-1832 Isaiah Hallock house on this site had burned down about ten years earlier. The family worked, saved their money and built this “four square” farmhouse about 1931–right in the middle of the Great Depression. Behind the house is the hand-dug well–about 70 feet deep. The well stonework was inserted from top down! The first floor interior has been restored as a 1930s Polish farmhouse.
28. Cichanowicz Garage. The Cichanowicz family built this garage around 1938 to store and service farm vehicles. For many years, a large gas pump stood by the southwest corner. Also notice the heirloom “Dr. Van Fleet” rose that has been growing there since the early 20th century.
29. Naugles Barn. George Naugles was the son of a Polish-Lithuanian immigrant family. When the old barn burned to the ground in 1936, he replaced it with the fine new one we see today. It is configured in the traditional “English” barn style, with large doors on the broad north and south walls leading to the central thrashing floor and lofts on either side. Proceeds of the family’s Prohibition-era rum-running operation probably helped fund its construction. The barn was moved to this site in 1999 and has become the venue for our annual Spring Tea, Barn Dance, Long Island Fleece and Fiber Fair, Fall Festival, Christmas at Hallockville, charitable events and exhibits as well as becoming a popular rental for weddings and other affairs. Under the west side shed you will see a 1939 Model 917T Ford truck. The Cichanowicz farm owned a similar truck that appears loaded with cauliflower in an early 1940s photograph.
From here, you can also look toward the facilities of the Long Island Antique Power Association to the west. A sister organization to the Hallockville Museum Farm, LIAPA collects antique farm and power equipment of all types and its annual Tractor Pull is always an attractive use of Hallockville’s farm road.
Note that LIAPA in not open to the public.